IGBT (Insulated Gate Bipolar Transistor), insulated gate bipolar transistor, is a composite fully controlled voltage-driven power semiconductor device composed of BJT (bipolar transistor) and MOS (insulated gate field effect transistor), which also has MOSFET The advantages of high input impedance and low on-voltage drop of GTR. The saturation voltage of the GTR is reduced, the current-carrying density is large, but the drive current is large; the MOSFET drive power is small, the switching speed is fast, but the conduction voltage drop is large, and the current-carrying density is small. IGBT combines the advantages of the above two devices, with low driving power and reduced saturation voltage. It is very suitable to be used in converter systems with a DC voltage of 600V and above, such as AC motors, frequency converters, switching power supplies, lighting circuits, traction drives and other fields.
IGBT insulated gate bipolar transistor is a typical bipolar MOS composite power device. It combines the power MOSFET process technology to integrate the power MOSFET and the power tube GTR in the same chip. The device has the characteristics of high switching frequency, large input impedance, good thermal stability, simple drive circuit, low saturation voltage and large current. It is widely used as a power device in industrial control, power electronic systems and other fields (for example: servo motor Speed regulation, variable frequency power supply). In order to make the system we designed can work more safely and reliably, the protection of IGBT is particularly important.
At present, in the process of using and designing IGBTs, the extensive design mode is basically adopted-the required margin is large, the system is huge, but it is still unable to resist external interference and various failure problems caused by its own system . Shunlei Electronics uses its production and design advantages in the semiconductor field, combined with the characteristics of transient suppression diodes, and breaks through the design bottleneck by integrating the internal and external systems on the basis of studying the failure mechanism of IGBTs. This article will break through the traditional protection methods and discuss the solution of IGBT system circuit protection design.
IGBT failure occasions: from inside the system, such as the distributed stray inductance of the power system, motor induced electromotive force, and load mutations will cause overvoltage and overcurrent; from outside the system, such as grid fluctuations, power line induction, surges, etc. In the final analysis, IGBT failure is mainly caused by the overvoltage/overcurrent of the collector and emitter and the overvoltage/overcurrent of the gate.
IGBT failure mechanism: IGBT is short-circuited due to the above reasons, and a large transient current will be generated-the current change rate di/dt is too large when it is turned off. The existence of leakage inductance and lead inductance will cause overvoltage of the IGBT collector, which will generate a holding effect inside the device, which will make the IGBT lock failure. At the same time, a higher overvoltage will cause the IGBT to break down. The IGBT enters the amplifying area due to the above reasons, which increases the switching loss of the tube.
IGBT traditional failure prevention mechanism: minimize the wiring inductance and capacitance of the main circuit to reduce the turn-off overvoltage; place a freewheeling diode between the collector and the emitter, and connect the RC circuit and RCD circuit, etc. ; On the grid, select the series impedance reasonably according to the circuit capacity, and connect the Zener diode in parallel to prevent grid overvoltage.
IGBT failure protection
1. Collector over-voltage and over-current protection, taking the main circuit of IGBT variable frequency speed regulation power supply as an example (Figure 1).
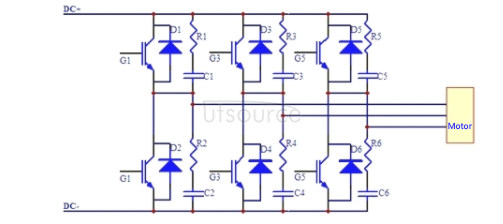
Figure 1: Traditional IGBT protection mode.
The RC filter circuit is connected in parallel between the collector and the emitter, which can effectively suppress the turn-off overvoltage and switching loss. However, in practical applications, because the surge surge at the front end of the DC power supply will cause the collector overvoltage and make the suppression effect of the RC filter circuit part effective, the IGBT will usually be broken down or short-circuited. In addition, when the motor is started, due to the large current when starting, the inductance distributed in the main circuit will also cause a greater degree of induced overvoltage, which will damage the IGBT. At the same time, the induced electromotive force caused by the excitation of the motor can cause considerable damage to the circuit-engineers often fail to take this into consideration.
In view of the above situation, the surge part can be protected by lightning protection circuit (Figure 2). The Blue Baby Surge Suppressor (BPSS) developed by Shunlei Electronics has both great overcurrent capability and extremely low residual voltage in terms of lightning strikes. At the same time, for the motor part, referring to the relevant standards of ISO7637, the product is fully usable. The use of other devices can not achieve the above two conditions at the same time. The specific problems are: varistors are prone to failure in the long wave (P5A) of ISO7637 and are not suitable for long-term use; ceramic discharge tubes cannot be directly used in active circuits, which often cause short circuits due to freewheeling problems and suppress excessive voltage.
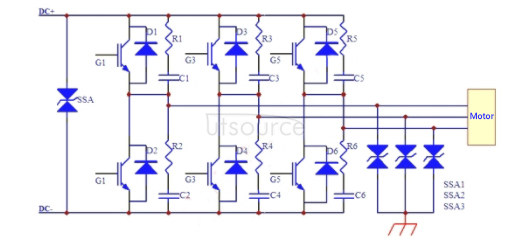
Figure 2: New IGBT protection circuit
2. Grid overvoltage and overcurrent protection
Traditional protection mode: The protection scheme prevents gate charge accumulation and gate-source voltage spikes from damaging the IGBT-some protection elements can be set between the G pole and the E pole. The function of the resistor RGE as shown in the figure below is to make the gate accumulated charge leak Amplifier (the resistance value can be 5kΩ); two voltage stabilizer diodes V1 and V2 in reverse series are to prevent the gate-source voltage spike from damaging the IGBT. In addition, there is also a design for isolation between the control circuit part and the driven IGBT, and the design of a driving pulse circuit suitable for the gate. However, even so, in the actual industrial environment, the above scheme still has a relatively high product failure rate-sometimes even more than 5%. Relevant experimental data and research show that this is closely related to transient surge, static electricity and high-frequency electronic interference, and the response time and current withstand capability of the Zener tube here are far from enough, which leads to overheating and damage to the IGBT.
New protection mode: Change the traditional Zener tube to a new type transient suppression diode (TVS). Generally, the gate drive voltage is about 15V, and SMBJ15CA can be selected. The product can pass the IEC61000-4-5 surge test 10/700US 6kV.
TVS has a very fast response speed (up to PS level), and its current capacity far exceeds Zener diodes (up to thousands of amperes). At the same time, TVS has a very good suppression effect on static electricity. The product can pass the IEC61000-4-2 contact discharge 8kV and air discharge 15kV discharge test.
Change the traditional resistance RG to a positive temperature coefficient (PPTC) fuse. It not only has the effect of resistance, but also is sensitive to temperature. When the internal current increases, its impedance also increases, which has a very good suppression effect on overcurrent.
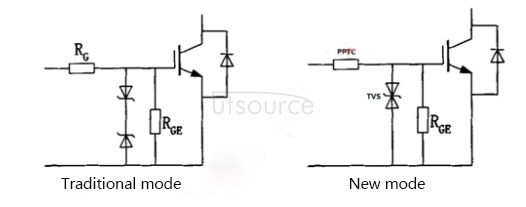
Figure 3: Circuit comparison between traditional protection mode and new protection mode.
Comments






























participate in discussions
Veuillez-vous Connecter ? to participate in the comments
New customer Start here.